Protecting Your PC and Online Accounts: Essential Steps for Enhanced Security
Are you also worried about the security of your PC and online accounts? Protecting your accounts and PC is essential to avoid scammers and hackers. Hackers are always trying to steal your personal information or try to harm your PC, so keep it as secure as possible.
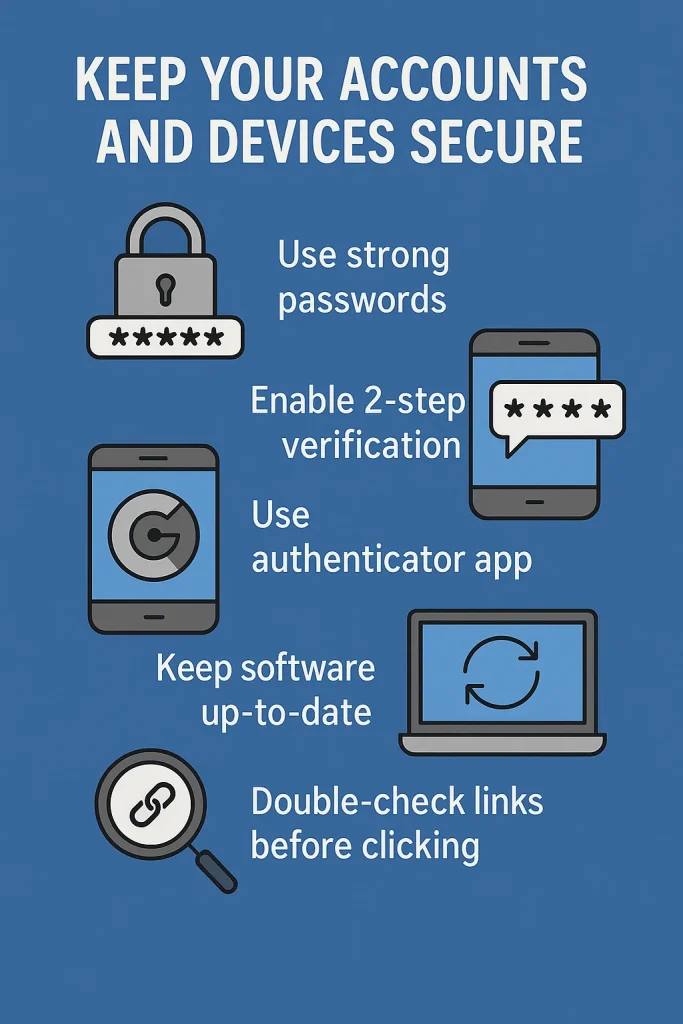
To stay safe, do these simple things: like use strong passwords, enable 2-step verification, and use the Google Authenticator app to enhance security. Also, keep your devices updated and always double-check links before clicking to avoid malware.
Read this complete advice to avoid malware, scams, or hacking to keep your online accounts and Devices secure.
Fundamentals of PC Security
To keep your computer safe and secure, it’s essential to know the typical threats it can face, make sure your operating system and security programs are always up to date, and use strong protections for your internet connection. Hackers usually take advantage of old software or weak spots in system files to harm it.
Understanding Malware and Threats
Malware is any type of malicious computer program or file that is designed to cause harm to your device or data. Cybercriminals are always trying to steal your sensitive information, interfere with operations, gain unauthorized access, and delete sensitive data using malware.
There are many types of malware threats, such as computer viruses, worms, adware, spyware, and ransomware. Malware can steal into your computer or phone in many sneaky ways. Here are the most common ones: If you plug in a USB or hard drive that’s already infected, the malware can enter your system automatically without you even clicking anything. Some websites on the internet look normal, but when you click on a link, share something, the website secretly puts bad software into it to steal your personal information.
You might get an email that looks real, but it has a harmful file or link. Once you click or download it, malware gets installed. Hackers can then steal your data, control your device from far away, or spy on your system. Some malware is really clever and hides itself from antivirus software. It may change its code again and again, or only work once it’s out of the safe testing zone (sandbox). Some don’t even save files on your computer; they run straight from memory, making them hard to find.
If you download apps or software from unofficial websites (not from the app store or the official site), you might end up installing malware along with it. These harmful programs can sneak in when you quickly agree to terms without reading.
System updates
Updating your phone, computer, or apps helps keep them safe and working well. These updates fix problems and protect you from hackers. They can also add new features that make your device better.
Hackers look for weak points in systems and apps to break into your device. Updates fix these weak points so hackers can’t get in easily. That’s why it’s smart to turn on automatic updates. So your device updates by itself without you needing to do anything.
Real-life example: Sehar was very busy and didn’t update her phone or computer for a long time. One day, she got an email with a strange link. At first, she ignored it. But later, she clicked on it out of curiosity. A virus infected her computer right away.
Her business had to stop because she couldn’t use her computer anymore. Sehar learned the hard way that if she had updated her device, it could’ve blocked the virus.
What You Should Do
- Always keep an eye out for updates.
- To keep your device safe, enable automatic updates.
- Update antivirus apps too, so they can catch new viruses.
- Updates also make your device run better and fix bugs.

Role of Firewalls in Protection
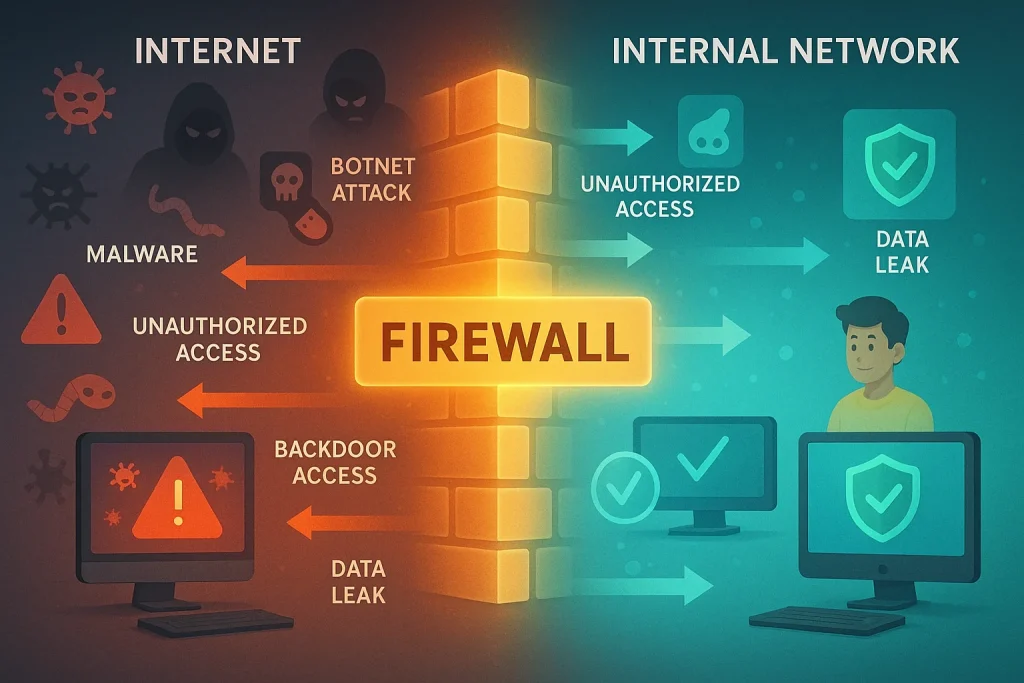
A firewall is a type of security system that uses pre-established rules to monitor and regulate all network traffic, both inbound and outbound. It serves as a firewall between untrusted external networks, such the internet, and trustworthy internal networks. Its primary goal is to permit lawful communication while preventing unwanted access.
What does a firewall protect you from?
A firewall can defend against:
- Unauthorized access: Blocks hackers or intruders from entering your network or device.
- Malicious traffic: Stops harmful data packets from reaching your system.
- Viruses and worms: Helps prevent the spread of malware that tries to exploit network vulnerabilities.
- Data leaks: Prevents sensitive information from leaving your network without permission.
- Botnet attacks: Stops your system from becoming part of a network of infected machines.
- Backdoor access: Blocks hidden ways attackers use to bypass regular security.
However, a firewall doesn’t provide full protection alone — it should be used along with antivirus software, strong passwords, and regular updates.
Securing Online Accounts
Online accounts are often targeted by hackers. Use strong passwords that combine letters, numbers, and symbols and have a minimum of 12 characters to protect your accounts. Avoid easy-to-guess details like names or birthdays. Use unique passwords for each account, especially important ones like email and banking.
1. How to Create Strong Passwords and Use Password Managers
Using strong passwords is the first step to securing your online accounts. A strong password should contain both capital and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols, and it should have a minimum length of 12 characters. Don’t use popular words or specifics like your name or birthday. Every account, especially crucial ones like your bank and email accounts, should have a different password.
Remembering many strong passwords can be hard, so use a password manager. Password managers safely store all your passwords in one encrypted place that only you can access. Additionally, they can generate secure, random passwords for you and have them automatically fill them in when you log in. This way, you don’t have to reuse passwords or write them down where someone else might find them.

2. Why Using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Is Important
Beyond merely using a password, multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides an additional degree of protection. Before logging in, you must submit two or more kinds of verification. For instance, you might need to use your fingerprint or input a code that is texted to your phone after entering your password.
Even if hackers know your password, MFA makes it far more difficult for them to access your account. Many popular websites and apps offer MFA options, so always enable it on important accounts like email, social media, and banking. The chance of unwanted access is significantly decreased by taking this one step.

3. Using Standard User Accounts and Protecting Personal Information
Avoid using an administrator account on your computer for routine activities like reading your emails or browsing the web. Instead, use a standard user account, which limits what can be changed or accessed. This lessens the likelihood that hackers may seriously harm your account if they manage to get access.
Additionally, exercise caution while disclosing private information online. Avoid giving out full names, addresses, or birth dates on websites or apps unless they are trustworthy. Watch for signs of suspicious activity in your accounts, like unfamiliar logins, and never click on links or downloads from unknown sources. Taking these precautions helps keep your identity and data safe.

4. Protecting Personal Information and Monitoring Activity
Use caution when disclosing too much personal information online. Don’t divulge personal information on unreliable websites, such as your full name, address, or birthdate. Regularly check your account activity for unknown logins and never click suspicious links or downloads to stay safe.
5. Secure Your WiFi Network
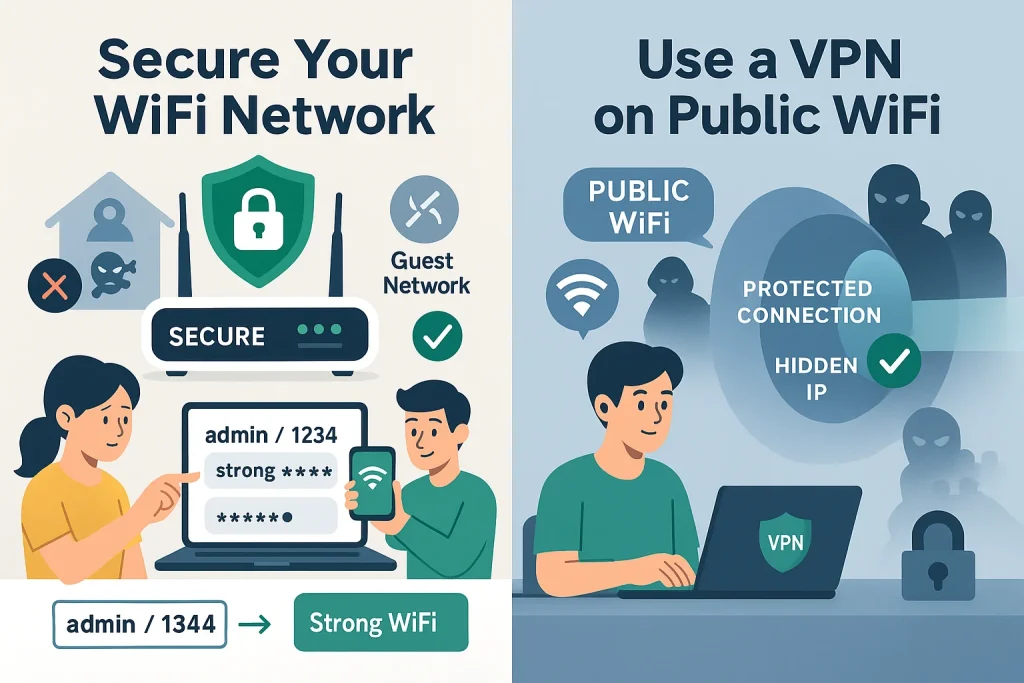
If your WiFi is not protected, anyone nearby could connect to it. This can allow strangers to misuse your internet for illegal activities or even try to access your personal data. To keep your WiFi safe, it’s important to change both your WiFi password and your router’s login details.
To do this, first find your router’s IP address (like 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1) and type it into your web browser. This will open the router’s settings page. Routers come with default usernames and passwords that are easy for hackers to guess, such as “admin/admin” or “admin/1234.” You should change these to something strong and unique.
Also, change the password you use to connect devices to your WiFi. Make this password long and hard to guess. For extra safety, create a separate guest network for visitors, so you don’t have to share your main WiFi password with them.
6. Use a VPN When on Public WiFi
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) helps protect your online information when you connect to the internet, especially on free or public WiFi. It works by encrypting your data, which means no one else can see what you are doing online.
VPNs also hide your real IP address, making it harder for anyone to track your location or identity on the web. You can find VPN apps for your phone or computer, so you can stay protected wherever you go.
Public WiFi networks are often unsafe because anyone else using the same network might try to spy on your connection. Using a VPN stops others from seeing your data and helps keep your accounts and personal info secure.
Advanced Protection Strategies
Protecting your digital presence involves more than just creating strong passwords. It requires a proactive approach to identify threats, use effective security tools, and safeguard your personal and business information from cyber attacks.
Identifying and Preventing Phishing Attacks
Phishing attempts try to deceive you into sharing sensitive details such as passwords or financial information by pretending to be trusted sources. These often arrive as emails or messages containing suspicious links or urgent requests. Signs to watch for include poor spelling, unfamiliar sender addresses, and pressure tactics urging immediate action. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources; instead, visit official websites directly. Utilizing email filters and browser security add-ons can also help detect and block fraudulent attempts.
Anti-Malware and Real-Time Threat Protection
Installing reliable anti-virus and anti-malware programs is essential to protect your devices from malicious software. These applications continuously scan for threats and prevent infections by blocking harmful downloads and suspicious files. Keeping these tools updated ensures they recognize the latest threats. Advanced protection solutions offer additional safeguards such as real-time threat analysis and blocking unauthorized software installations.
Encryption for Secure Data Handling
Encryption transforms your data into an unreadable format unless decrypted with the correct key, protecting information stored on your devices or transmitted over the internet. Activating encryption on your devices and using secure messaging platforms helps prevent unauthorized access to personal and sensitive data. This layer of defense is especially important for anyone who handles confidential or private information regularly.
Google’s Advanced Protection Program
Google offers an enhanced security option designed to shield high-risk users, like journalists or activists, from targeted cyberattacks. This program requires physical security keys or passkeys for account access, which helps prevent unauthorized logins even if someone knows your password. It also enforces strict controls on app permissions and screens downloads to avoid malicious files. Such comprehensive protections make it much harder for attackers to compromise your Google account.
Endpoint Security for Businesses
Modern businesses face complex cyber threats that basic antivirus software can’t fully address. Endpoint protection solutions combine multiple defense layers—including malware detection, firewalls, and network monitoring—to guard devices and data from sophisticated attacks. Incorporating technologies like machine learning enables the system to detect suspicious behaviors and new threats more effectively.
Network and Cloud Security Measures
Securing your network involves tools such as intrusion detection systems that monitor unusual activities and VPNs that encrypt data transmissions, especially for remote users. Cloud security is enhanced by encryption, access controls, and tools that prevent sensitive data from being accidentally or maliciously leaked. Regularly assessing third-party vendors also helps reduce risks associated with external partnerships.
Compliance and Legal Safeguards
Adhering to data protection laws such as GDPR and HIPAA is vital for legal compliance and protecting customer data. Organizations must be prepared to notify affected parties promptly if a breach occurs. Safeguarding intellectual property through both legal protections and cybersecurity practices is also crucial to maintaining competitive advantages.
Emerging Technologies in Cybersecurity
New technologies are reshaping security strategies. Blockchain provides tamper-resistant records, ensuring data integrity. Artificial intelligence and machine learning improve threat detection by analyzing vast datasets for suspicious patterns. Quantum cryptography promises future-proof encryption methods to protect against the evolving capabilities of quantum computing.
